Web Application Testing Tutorial: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples And Best Practices
Web application testing is an approach to ensure the correct functioning and performance of the web application by following a structured process.
With web application testing, detection of bugs or errors is done, and ensure that all such are removed before the web application goes live.
The primary purpose of web application testing is to fix any issues and vulnerabilities in the web application before it is released on the market. With this test, you can ensure the web application meets all the end-user requirements and provide a high-quality experience. However, it is important to conduct web application testing with accuracy.
Understanding Web Application
Web applications are application programs with interconnected modules which are loaded on the client side and delivered over the Internet through the browser interface. Developers build web applications for different uses, and their users vary from organization to individual. The commonly used web applications are webmail, online calculators, and eCommerce shops.
Which web technologies are used in building web applications? They are mainly HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript. HTML uses tags to find different elements and their interaction.
On loading a web page, HTML is compiled into a Document Object Model (DOM) that shows its structure. CSS is a style description framework mainly used to style and format visual elements of web applications. Further, JavaScript is a high-level scripting language upon which all dynamic behavior of web applications is scripted and executed.
In addition to the above technologies, JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, and Vue are used as they give ready-to-use tools and libraries. This simplifies the process of making a complex user interface.
CSS Preprocessors like LESS and SASS allow writing and organizing CSS code efficiently. It gives features like variables, mixins, and nesting, allowing developers to maintain a reusable style across web applications. Also, the HTML templating simplifies generating dynamic HTML content.
In addition, web applications also have a backend or server-side layer, which comprises APIs built using databases. It abstracts the relevant information into contracts that can be accessed by the front end through HTTP methods using appropriate requests and credentials.
By combining these various technologies, web applications can deliver a seamless user experience with rich functionality and interactivity. The front-end technologies handle the visual presentation and user interaction, while the back-end technologies manage the data and business logic. The collaboration of these technologies enables the creation of powerful and dynamic web applications.
Now let us learn about different types of web applications. It will help you get an idea of testing these applications.
Test your web apps across 3000+ real desktop and mobile browsers. Try LambdaTest Now!
Type of Web Applications
Different types of web applications vary in their function. Here are some of those:
Static web apps: These web applications are stored on a server, and when you visit them, they look exactly as they are. You can think of them as simple websites like portfolios or landing pages.
Dynamic web apps: These web applications are more interactive and fetch real-time data based on your request. They have databases on the server side that provide updated information to you.
Dynamic web apps can be further divided into several types:
Single-page apps: These web applications don't load new pages when you navigate. Instead, they rewrite the current page on the fly. An example of this is the Gmail app, where you can read, reply, and organize your emails without having to load separate pages.
Multi-page apps: These web applications work by loading new content from the server whenever you perform a new action. Websites like Amazon and CNN are good examples of multi-page apps. Each time you click on a link or perform an action, a new page loads with updated information.
Portal web apps: These web applications provide you with a range of categories on their home page. They often have features like a shopping cart or a user profile. Student portals or patient portals offering various services or information are portal web apps.
Progressive web apps: These web applications are designed to give you a native app-like experience across different devices. They utilize features available in web browsers and mobile devices to provide a seamless experience. Spotify and Pinterest are examples of progressive web apps.
eCommerce web apps: As the name suggests, these web applications are nothing but online stores that you use daily for purchasing goods. This web application helps you search for products, add them to a cart, make transactions, and complete purchases. Amazon and Flipkart are popular examples of eCommerce web apps.
Animated web apps: These web applications go beyond the usual features of web apps and use animations to present content engagingly. Websites like Apple or Squadeasy incorporate various animated effects to make their interfaces more visually appealing and interactive.
Rich Internet apps: These web applications are used by organizations to overcome restrictions imposed by web browsers. They mainly rely on plugins like Flash or Silverlight and give features similar to desktop applications. Adobe Flash and Microsoft Silverlight are examples of rich Internet apps.
JavaScript (JS) web apps: These web applications are built using JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React.js, and Vue.js. They provide enhanced user interaction and are optimized for search engines. Many client portals, such as LinkedIn and Uber, are implemented as JavaScript web apps.
As we are now aware of web applications and their types, it is crucial to know why testing web applications is important.
What is Web Application Testing?
Web application testing is the process of evaluating and assessing all aspects of a web application’s functionality, like detecting bugs with usability, compatibility, security, and performance. This testing practice ensures the quality of the web application and its working as per the end-user requirements.
It systematically checks and verifies the web application's components and features to ensure a positive user experience. This systematic approach performs various tests to detect any issues, bugs, and vulnerabilities that might affect web applications' performance and security. Some of those tests are functional testing, performance testing, security testing, etc. The QA teams and testers mainly conduct it by simulating real-world scenarios and user interactions to verify the web application’s behavior and ensure its reliability.
The main goal of web application testing is to uncover and rectify any issues and weaknesses in the web application and lower the incidence of data breaches or system failure. With web application testing, developers can check that the developed web application meets the required standards and delivers a seamless user experience.
Now let us learn the significance of web app testing to get a better idea.
Why is Web Application Testing Important?
In this digital world, the use of web applications has risen tremendously as we enter the year 2023.
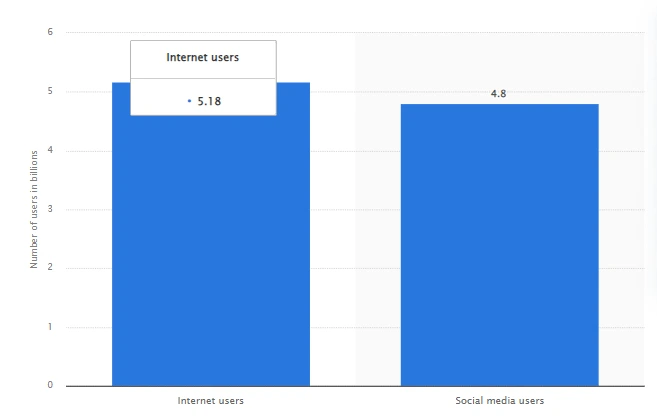
As per the report of Statista, it is evident that there are 5.18 billion Internet users as of January 2023, which accounts for 64.4% of the global population. With the rise in the use of the Internet by people, access to web applications has surged. It has become an essential part of our daily lives.
We use them for online shopping, social media, banking, entertainment, and other means. However, any bug or error in the web applications can interfere with their usability and function, making them low-quality.
But have you ever wondered how these applications are tested to ensure they work flawlessly and provide a great user experience? That's where web application testing comes in. It ensures that your web applications work correctly when rendered across multiple browsers, devices, and operating systems combinations.
Benefits of Web Application Testing
In this section, let’s discuss the benefits you can expect while performing web application testing.
Improves app efficiency
Executing web application testing is an integral approach to ensure the efficiency and quality of the web application. You can check how well the web application can handle a large number of users, check its reliable function, and give smooth navigation.
Enhances user experience
GUI (Graphical User Interface) testing focuses on the visual aspects of the web application. It ensures that the user interface is designed with the end users in mind, meeting their expectations and preferences. GUI testing detects and addresses common UI defects such as font inconsistencies, color issues, and navigation problems. Enhancing the user experience makes the app more appealing, leading to a higher conversion rate of users into customers.
Improves app scalability
Load testing is a type of testing that verifies the performance of a web application under various user loads. By simulating a large number of users accessing the app concurrently, load testing helps identify performance bottlenecks. It ensures that the app can handle high traffic volumes without slowing down or crashing. This improves the application's scalability, enabling it to handle peak usage times efficiently.
Prevents data breaches
Security testing is crucial for web applications to protect sensitive user data and maintain customer trust. It involves identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities and threats that could lead to data breaches. By conducting security testing, web applications can be safeguarded against attacks and unauthorized access, ensuring the privacy and integrity of user information.
Ensures cross-platform compatibility
Compatibility testing is performed to ensure that web applications work seamlessly across different operating systems and web browsers. It verifies that the app's functionality, layout, and performance remain consistent across various platforms. By ensuring cross-platform compatibility, web apps can reach a wider audience and provide a consistent user experience regardless of the device or browser used.
Increases user conversions
Usability testing focuses on optimizing the user experience of a web application. It involves testing the app's features, navigation, and overall usability to ensure that users can easily interact with the app and consume its content. By identifying and addressing usability issues, web apps can provide a smooth and intuitive user experience, leading to increased user engagement and higher conversion rates.
Web vs. Desktop vs. Mobile Application Testing
At first glance, it might sound similar when looking at web application testing, desktop application testing, and mobile application testing. But when you delve into its concept, you will come to know about its major difference.
Here are some common differences between the three to clear your concepts.
| Factors | Web Application Testing | Desktop Application Testing | Mobile Application Testing |
| Aim | Verifies the working of the web application across different browsers. | Verifies the working of the desktop application across different computers and systems. | Verifies the quality of the mobile app performance on various devices and OS. |
| Focus | It necessitates familiarity with OS and databases. | It needs a crucial understanding of user interaction with the application. | It requires an understanding of the real mobile devices and their support on the application. |
| User interface | It has a web-based interface. | It has a native desktop interface. | It has a native mobile interface. |
| Connectivity | Requires Internet connection. | Work offline and online. | Requires Internet connection. |
| Device access | Access through web browsers. | Access directly on the desktop. | Access on the mobile device. |
| Hardware | Minimal hardware requirements. | Depends on desktop hardware specifications. | Depends on mobile device hardware. |
| Installation | Not required. | Required installation on the desktop. | Installation is needed on mobile devices. |
| Performance | Depends on network and server response. | Less dependency on network and server. | Can be affected by device performance. |
However, the differences mentioned above are just general in terms, but there might be some specific differences based on the involved software application and technologies.
Web Application Testing Scenario
Web application testing is performed in different types of conditions and scenarios. When you start with a web application, a test scenario should be kept in mind so that all the features and aspects of web applications are tested.
These scenarios are essential for ensuring the web application's quality, functionality, and usability. Some of those scenarios are as follows:
User Navigation Flow:
Test the user's ability to navigate smoothly between different website pages.
Verify that links, buttons, menus, and navigation elements work as expected.
Checkbox and Radio Button Selection:
Ensure users can correctly select and deselect checkboxes and radio buttons.
Validate that the selected options are properly recorded and displayed.
Dropdown List Selection:
Test whether users can choose the desired values from dropdown lists.
Verify that the chosen values are accurately captured and used within the application.
Command Button Functionality:
Validate the functionality of various command buttons, such as Save, Next, Upload, Reload, etc.
Ensure that these buttons perform the expected actions and update the application accordingly.
Search Functionality:
Test the search functionality across different web pages.
Verify that the search feature returns accurate and relevant results based on user queries.
Broken Link Verification:
Check for any broken links within the web application.
Ensure all links are valid and lead to the intended pages or resources.
Tab Order Functionality:
Test the tab order across pages, determining the focus sequence when users navigate using the keyboard.
Verify that the tab order is logical and consistent, allowing for easy navigation and accessibility.
Default Value Display:
Ensure the web application correctly displays default values on each web page.
Verify that these values are correctly pre-filled or selected for users' convenience.
Email Functionality:
If the web application involves email communication, for example, in a situation like a password reset, you should test the email functionality.
Ascertain the success of the emails after they are sent, considering the accuracy of the content and appropriate recipients.
Phases of Web Application Testing
The web application testing life cycle is a structured approach to testing the web application’s reliability and quality. It follows a series of phases that help identify defects, ensure functionality and assess web application performance. These are the different phases involved in web application testing:
Requirement gathering: In this phase, QA teams collect all requirements related to web application features. They initially conduct reviews and analyze the need and specifications of the web applications. This helps them to identify all the key features, functionality, and performance.
Test planning: Here, the QA team prepares and updates the test plan documents by defining the test scope, objective, entry, and existing criteria of web application testing.
Test case preparation: In this phase, test cases and test scenarios are created based on the end-user requirement and test objective. Additionally, inputs, expected outputs, test data for each test case, testing techniques, and methodologies are identified. Test environment set-up is also done, which includes configuration of hardware, software, and network configuration to simulate the real-world scenario.
Test execution: After preparing for the test, testers run the test cases as per the plan. This involves performing functional testing, usability testing, regression testing, etc. They also report any defect found and document deviation from the intended result.
Bugs reporting: When a test case fails during the execution of the testing process, the testers detect the bug and raise and report it using defect tracking tools like HP ALM QC and Jira. In other words, the testing team monitors and tracks the defects, assigns priorities, and collaborates with the development team to resolve them.
Defect retesting: The testing team prepares and shares test reports, which include details about the test coverage, test execution results, defect metrics, and overall quality assessment. In this phase, when the developer fixes the identified bug, the tester retests and re-executes the failed test cases to ensure its fixation.
Test closure: In the final stage, the testing team evaluates the overall testing process, identifies lessons learned, and prepares a test closure report. The test cycle is closed when all the defects are fixed and web applications function as expected.
The phases mentioned above of web application testing help ensure that web applications are thoroughly tested before being deployed to production. These phases are executed by two different approaches, which include manual and automation. Read the below section to learn more.
Web Application Testing Techniques
Web application testing includes different testing techniques and different forms of testing. Including all tests at different phases of web application testing is crucial. Here are the testing techniques which should be followed while performing web application testing.
Functional testing
Functional testing ensures that all web application functionalities are verified and specification requirements are met. Such tests are performed using test cases that confirm the functionality of each web application component.
Following are the checklists to be considered while performing functional testing:
Correct working of links in the desired manner.
Correct the working of buttons in the desired manner.
Verifies validation of the fields like mandatory checks, character limit checks, accepted character checks, and error messages.
Correct storage of data in the database during submission of the form.
Checks form fields are populating default values.
Checks integration between different modules of the system.
Type of Functional Testing
Functional testing is carried out through different levels of tests, which are discussed below:
Unit testing: Functional testing begins at the unit testing level, where the developers test each module or unit of the web application. Generally, the developers check the expected working of each unit of code and help in the early detection of bugs in the web application development process.
Integration testing: This type of functional testing involves a test of working different units of code together. In other words, in this level of testing, different components are integrated and tested together by the developers and testers. It can be executed using black box and white box testing techniques.
System testing: The next level of testing is system testing, where the testing team tests the whole web application. It mainly helps validate all end-user requirements before it is released to them. Here, all the included components of web applications and their interactions are tested.
Regression testing: This test here checks that any changes or updates made during system testing do not cause the web applications' non-functionality. It is mainly executed after every code change and ensures the web application's correct functioning.
Acceptance testing: It is the final testing level, where the final test is conducted to ensure that the web application meets the end-users requirements. End-users mainly execute it to check that all the required web application features are implemented correctly.
Non-Functional Testing
Non-functional testing in web applications focuses on evaluating aspects other than functionality. It examines performance, usability, security, reliability, and scalability.
This type of testing assesses how well the web application performs under different conditions, such as high user loads or varying network speeds. It also verifies if the application meets industry standards and compliance requirements.
Non-functional testing aims to ensure the web application delivers a seamless user experience, performs optimally, and meets the expected non-functional requirements to meet user expectations and business needs.
UI Testing
In UI testing, critical components of web applications are tested, which include the web server interface, database server interface, and application server interface. This helps to verify the interconnection relationship of all components of the web applications. It will ensure seamless communication and data flow between these servers.
Usability Testing
Usability testing aims at assessing the web application's user interface. It checks if the interface aligns with industry standards regarding effectiveness and user-friendliness. Following global conventions and web standards is crucial while developing a web application. Usability testing is particularly important for applications that aim to automate manual processes.
During usability testing, testers pay attention to specific critical factors such as correct navigation, a site map for easy browsing, and avoiding overcrowded content that can confuse end-users. The goal is to create an intuitive, user-friendly user interface that enhances the overall user experience.
Here are different types of usability testing used to test web applications:
Exploratory testing: This testing type involves exploring web applications with no particular goal in mind. It is undertaken to explore and comprehend the functionality and user interface of the web application.
Comparative testing: This involves a comparison of the usability of the web applications to different types of web applications. It helps identify the components where the developing web application falls short compared to its competitors in the market.
A/B testing: This test involves two versions of the same web application to find which gives a robust user experience. Such tests will help you detect particular elements of the web application which require optimization and improvement.
Remote usability testing: Such a test involves verifying the usability of the web applications with users of different geographical locations. Such tests give valuable insight into the user-friendliness of the web application.
Hallway testing: This test checks for the web application's usability by including people not from the development team. Its primary purpose is to test the web application from different perspectives of the included people. This not only ensures the quality of the web application but also helps find those usability issues which might mistakenly get missed by the team.
Performance Testing
Performance testing allows you to evaluate how well a web application can perform in different scenarios for various criteria like response time and interoperability. It involves different types of tests, such as stress testing and load testing, to assess the application's functionality under different testing scenarios.
Several types of performance testing can be used for web applications, including
Stress testing: It pushes the web application to its limits to see how it performs under extreme conditions. This test helps identify potential performance issues that may occur during peak usage.
Spike testing: It is helpful for web applications that experience sudden spikes in traffic, such as ticketing systems or e-commerce websites. It evaluates how well the web application handles these sudden bursts of activity.
Endurance testing: It assesses the applicant's ability to manage a constant load over an extended period. This type of testing is relevant for web applications that are expected to be used continuously.
Volume testing: It is particularly valuable for web applications that deal with large amounts of data, such as data analytics or database management systems. It tests the application's ability to handle and process a significant volume of data efficiently.
Scalability testing: It focuses on assessing the web application's ability to handle increasing numbers of users or data as the application grows over time.
Following are the checklists to be considered while performing performance testing:
Check the performance of web applications when being used by multiple users simultaneously.
Check the performance of web applications when single functions are being used by multiple users simultaneously.
Response time of web applications on different Internet speeds should be verified.
Check the performance of web applications on switching Internet connection between two or more networks.
Check whether the web application can save data in the event of a system crash.
Compatibility Testing
Compatibility testing is the process of testing web applications that ensure that they work and function seamlessly across different web browsers, OS, and hardware platforms. Such a test is mainly performed to check and verify whether the web application meets user experience on diverse types of devices and environments.
Different types of compatibility testing include the following:
Browser compatibility testing: Such testing method checks the function and compatibility of the web applications across different types of web browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and Safari. It considers testing of layout, design, and function of the web application in each of the specific browsers.
Device compatibility testing: With the increasing use of mobile devices, it has become crucial to test the working of web applications on those to give a seamless experience to users. Device compatibility testing allows checking the web application on different screen sizes, resolutions, and OS of the different devices.
Operating system compatibility testing: This testing verifies if the web application operates smoothly on various operating systems such as Windows, Mac, and Linux. It aims to maintain consistent functionality, performance, and appearance across different operating systems.
Network compatibility testing: This testing evaluates how the web application performs under different network conditions. It checks if the application remains usable and responsive in low bandwidth or high latency scenarios, ensuring a good user experience regardless of network limitations.
Database compatibility testing: This testing ensures the web application seamlessly works with different database systems. It examines the application's functionality and performance when interacting with databases like MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL.
Following are the checklists to be considered while performing compatibility testing:
Check the web application on different OS and browsers like Chrome, Mozilla, and others in different scenarios:
Ensure font size, family, and spacing.
Ensure placement of fields and text on the screens.
Check for any error messages, tooltips, and placeholders.
Security Testing
This test type finds any security flaws in the web application and ensures it is safe and secure against online threats. The main goal of a security test is to identify any security risk and vulnerability with timely fixing before it is released in the market.
Penetration testing: Also known as pen testing, this testing simulates an actual attack on a web application. The goal is to uncover vulnerabilities and assess the security measures' effectiveness. It can be done manually or with the help of automated tools, and it helps you understand how well our application can withstand attacks.
Security scanning: With security scanning, we test web applications specifically for security-related problems. This could be misconfigured security settings or insecure network configurations. With this, you can discover potential weaknesses in the application's security and take steps to strengthen them.
Security auditing: This testing involves comprehensively reviewing a web application's security controls and processes. The aim is to identify any potential vulnerabilities and suggest improvements. It ensures that the security measures are adequate and effective in safeguarding the application.
Ethical hacking: Ethical hacking is a unique approach where professional hackers, who follow ethical guidelines, attempt to breach a web application's security. The purpose is to find any vulnerabilities other testing types may have missed. By performing ethical hacking, we can uncover hidden weaknesses and enhance the application's overall security.
Following are the checklists to be considered while performing security testing:
Check access to the web application’s restricted function by only authorized users.
Whether it uses secure protocols like HTTPS.
Ensure storage of confidential data like passwords and payment information of users in an encrypted format.
Verifies the use of strong password policies.
Ensures that any deactivated users do not access web applications.
Verifies the cookies do not store passwords.
Ensure the end of the session on clearing the cache.
Ensure logged out from the web application at the end of sessions.
Approaches to Web Application Testing
Web application testing, being a subset of software testing, enables developers to verify whether there are any bugs and errors in the application. Primarily, it is executed by two different approaches:
Manual Testing
Manual testing of web applications is needed when in-depth testing is required. It involves executing test cases manually without relying on automated testing tools. They carefully examine every aspect of the application to identify any flaw affecting its usability.
When manually testing a web application, testers simulate real-world usage scenarios. They click buttons, fill out forms, navigate through different pages, and perform various actions to ensure everything functions smoothly. With this, organization can validate their web application and assess important factors like accuracy, completeness, user-friendliness, efficiency, and more. It is often the initial step in creating user-friendly and intuitive interfaces.
Automation Testing
Web application testing using an automated approach involves testing with the use of automation testing frameworks with minimal requirement of human effort. Technically, automation testing of web applications refers to using automated tools and scripts to execute test cases and validate the web application's functionality, performance, and usability.
These scripts simulate user actions like clicking buttons, filling out forms, and navigating through different pages. To perform automation testing of web applications, testers utilize specialized testing frameworks and tools such as Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright. These tools provide features like recording and playback, script creation, element identification, and reporting capabilities.
However, it's important to note that not all tests can or should be automated. Automation testing is most effective for repetitive tasks, large-scale projects, and scenarios where a high level of accuracy is required. Certain aspects of testing, such as usability evaluation or exploratory testing, still benefit from manual intervention and human judgement.
Factors to Consider in Web Application Testing
When you begin with web application testing, certain factors should be considered to ensure successful test completion. Here are six key factors to look for in web app testing.
Evaluate HTML Page Interactions, TCP/IP Communications, and JavaScript:
Assess how diverse HTML pages interact with each other and the server.
Checks TCP/IP communications to ensure proper data transfer and communication between the web application and the server.
Evaluate the functionality and correctness of JavaScript code used within the web application.
Validate Applications for CGI Scripts, Database Interfaces, Dynamic Page Generators, etc:
Verify that any CGI scripts (Common Gateway Interface) used in the web application function correctly and securely.
Test the database interfaces to ensure proper data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
Check dynamic page generators to ensure they generate and display content accurately.
Test Web Applications across Browsers, Operating Systems, Localization, and Globalization:
It is important to test the web application on different web browsers (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) and operating systems (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux, etc.) to ensure compatibility and consistent behavior.
Additionally, assess the web application's localization and globalization capabilities by testing different languages, character sets, and regional settings.
Test Web URLs for Proper Functioning:
Verify that all web URLs within the application work perfectly, leading to the intended pages or resources.
Check for any broken links, redirects, or errors in URL handling.
Check for Typos, Grammar Mistakes, and Incorrect Punctuation:
Verify the web application's content or included information for typos, spelling errors, grammar mistakes, or incorrect punctuation.
Ensure clarity, accuracy, and consistency of the text and overall language used in the web application.
Map Old Pages to New Pages to Avoid Content Loss During Transition:
If the web application undergoes any updates, redesigns, or restructuring, ensure that old pages are correctly mapped or redirected to new ones. This helps prevent users from encountering broken links or losing access to valuable content during the transition process.
Why is End-to-End Web Application Testing a Priority?
When you have considered all the crucial factors in testing web applications; next, you have to ensure that they are end-to-end tested. This will provide complete information on the quality of web applications and identify and fix all the bugs and errors. Here are some other reasons why end-to-end web application testing should not be ignored.
Ensuring functional integrity: End-to-end testing validates a web application's entire flow and functionality, including all the interconnected components and systems. Testing the complete user journey helps ensure the application functions as expected.
Identifying integration issues: Web applications often rely on integrations with various systems, databases, APIs, and third-party services. End-to-end testing helps uncover any issues or failures in these integrations, ensuring smooth communication and data exchange between different components.
Validating user experience: It allows organizations to assess the user experience and ensure its alignment with the preferred standards. This allows the detection of any usability issues and navigation challenges, providing a positive and satisfying end-user experience.
Detecting performance bottlenecks: You can easily identify performance issues due to interactions between different components or external systems as you simulate real test scenarios. This will help to evaluate the web application's performance, scalability, and responsiveness.
Enhancing reliability and stability: End-to-end testing contributes to the overall reliability and stability of the web application. Thoroughly testing the application from end to end helps identify and fix bugs, errors, or vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of application failures or security breaches.
Web Application Testing Tools
Web application testing using the automation approach saves lots of time in the testing process. It ensures the fixation of errors and bugs at an early stage. The use of automation testing tools can help in accomplishing this. Here are some tools that can be leveraged to automate the web application testing process.
Selenium: Selenium is an open-source test automation tool widely used for web application testing. It provides automation capabilities across multiple operating systems, such as Windows, Mac, and Linux, and popular web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. Selenium allows testers to write test scripts in various programming languages like Java, Python, and C#, making it flexible and adaptable for different testing needs.
Cypress: Cypress is an open-source testing tool specifically designed for testing web applications built on JavaScript frameworks. It allows QA engineers to write tests using JavaScript, providing real-time execution and simultaneous viewing of test cases being created. Cypress offers a rich set of features for easier debugging, time-traveling, and stubbing network requests, making it popular among developers and testers for its simplicity and efficiency.
Playwright: Playwright is an open-source tool for browser automation and testing of web applications. It supports multiple web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, etc. Playwright offers APIs for automating web interactions and performing tests in various programming languages such as JavaScript, Python, etc.
It focuses on providing reliable cross-browser testing ability and supports headless and UI testing scenarios.
Puppeteer: Puppeteer is another popular open-source tool for browser automation developed by Google. It allows developers and testers to control and interact with web pages programmatically. Puppeteer provides a high-level API for automating tasks like generating screenshots, PDFs, and crawling pages.
It supports Chrome and other Chromium-based browsers and is commonly used for web scraping, testing, and generating performance reports.
Note : Run your Selenium scripts in parallel.Try LambdaTest Today.
How to Perform Web Application Testing?
Web application testing requires some preparation before digging into the actual testing process. This will help you get all aspects of testing web applications in one place and pipeline to have a systematic approach to the testing process.
Initiation of web application testing needs some prior preparation which ensures that the testing process is aligned with the project objectives and the test environment is accurately set up. A clear test strategy is in place to guide the testing efforts. Here are the steps to be followed for preparing for web application testing:
Identify Test Objectives: When starting with a web application test, the first thing you have to be clear about is its test objective and goal.
For example, it is important to identify the exact areas, key functionalities, and environments that must be tested. This will allow you to create effective test cases and ensure comprehensive coverage.
Establish Test Environment: Set up the test environment that closely resembles the production environment in which the web application will be deployed. This involves configuring the hardware, software, networks, databases, and other components required to replicate the deployment environment. A well-prepared test environment helps conduct realistic tests and identify potential issues early on.
Define Test Strategy: Develop a test strategy that outlines the approach, methodologies, and techniques to be employed during the testing process.
This includes determining the types of tests to be performed (e.g., functional, performance, security), selecting appropriate testing tools and frameworks, establishing test timelines and milestones, and defining roles and responsibilities within the testing team. A well-defined test strategy ensures a systematic and structured approach to web application testing.
After you have prepared for the test and know everything about what and how to test, you have to move to the actual testing process. Web app testing can be performed on a local computer or in the cloud, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Testing on a local machine provides greater control over the testing environment. Teams can customize the infrastructure and tools to meet their specific requirements, resulting in faster testing cycles without network latency. As a result, more resources will be required to help scale up to larger scenarios.
In contrast, cloud-based testing offers virtually unlimited resources and scalability without hardware limitations. Additionally, this method is cost-effective since teams pay only for the resources they need.
Web Application Testing on the Cloud
Web application testing in the cloud means that web applications are deployed and tested on cloud-based servers and resources. But why test on the cloud even though we have so many automation testing frameworks and tools in the market which allow web app testing?
The cloud-based platform offers several benefits which ease your web application testing process. You can scale up and down the testing environment according to the testing needs. You can access the web application from anywhere with an Internet connection, facilitating remote collaboration and enabling teams to work seamlessly across different locations.
The focus on web applications has surged the testing tools and platforms standard. You can leverage the true capability of web application testing by performing the test on a cloud-based platform like LambdaTest.
LambdaTest is a cloud-based digital experience testing platform that offers both manual and automated web application testing across 3000+ real browsers, devices, and OS. This allows cross browser compatibility testing of the web applications. It will ensure that web applications work flawlessly for all your users, regardless of their preferred browser or operating system.
Further, LambdaTest integrates with automation testing frameworks like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, etc. This integration allows you to perform automated testing on a secure, scalable, and reliable automation cloud platform. What else?
Now let us learn how to perform web application testing using the LambdaTest platform.
Real-Time Web Application Testing
With LambdaTest, testers can perform real-time browser testing on cloud infrastructure, enabling checking compatibility across different browser and operating system combinations.
Here are the steps to follow to perform Real-Time testing
Step 1: Sign up for free on LambdaTest and login to your account.
Step 2: Select the Realtime Testing card from the Modal box.
It will launch the Real Time Browser Test console.
Step 3: Here, you get two options for testing: Browser Testing and App Testing. Select Browser Testing from the left sidebar menu and enter the URL.
Choose the testing type (Desktop/Mobile), and select browsers, VERSION, BRAND, and OS. Then click on START.
It will launch a cloud-based machine allowing you to perform web application testing based on test configuration.
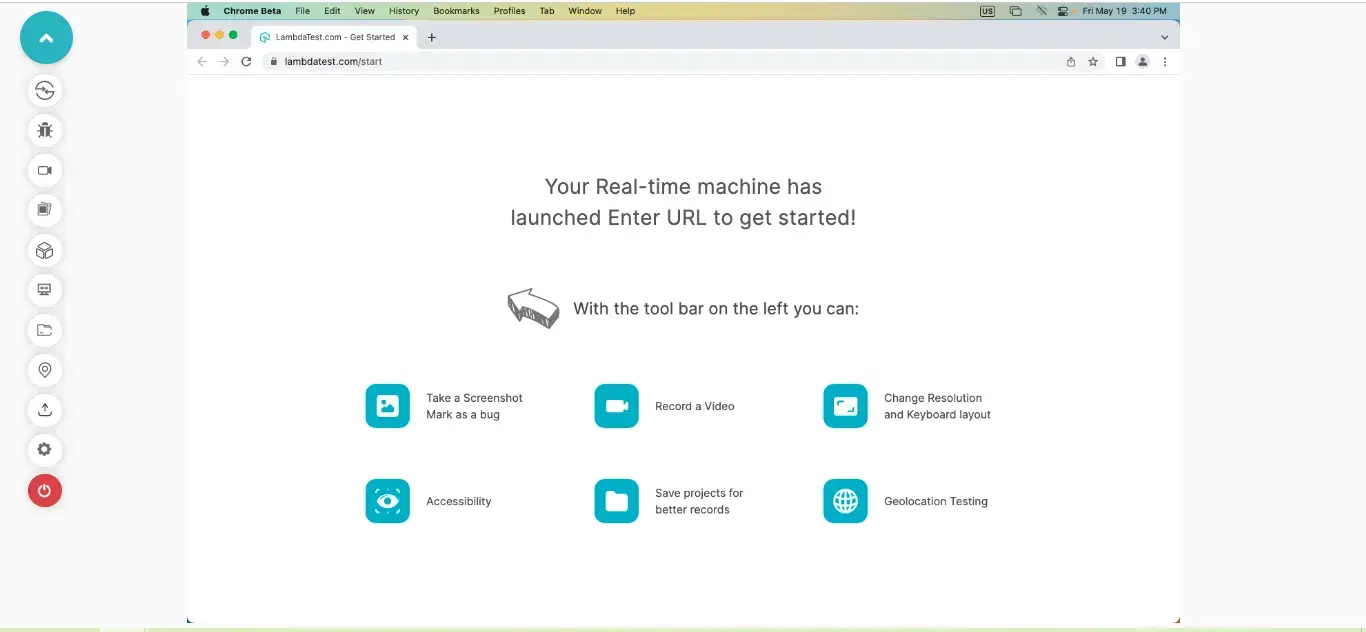
Web Application Testing on Real Device
You can test your web application on real devices, ensuring its function on various real devices.
Here are the steps to follow to perform real device testing
Step 1: Log in to LambdaTest as explained above.
Step 2: Select the Real Device Testing card from the Modal box.

Step 3: For Browser Testing on a real device and enter the URL, choose DEVICE TYPE, DEVICE, OS, and BROWSER. Then click on START.
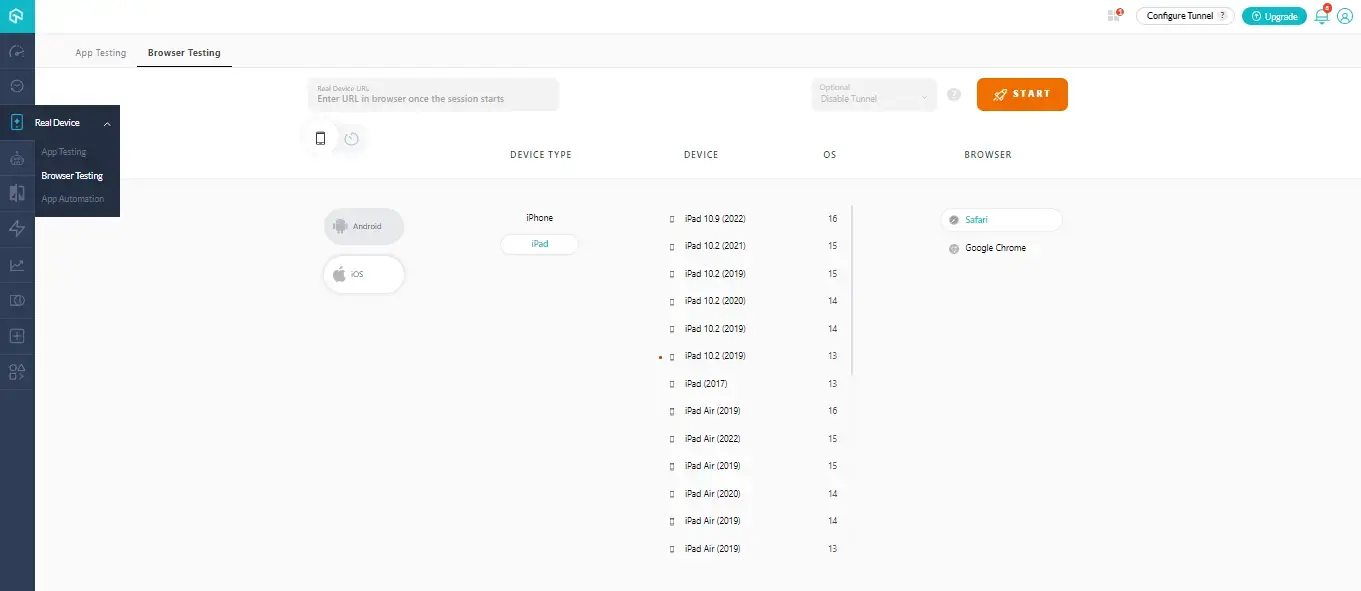
It will launch your web application on real device cloud infrastructure. Now you can perform your test.
Automated Web Application Testing
With LambdaTest’s online cloud Grid, you get access to 3000+ desktop and mobile environments to run Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and others to execute automation testing.

Subscribe to the LambdaTest YouTube Channel and stay up to date with the latest tutorials around Selenium testing, Cypress testing, and more.
Here are the steps to follow to perform automation testing
Step 1: Follow the same login process as explained above.
Step 2: Navigate to the Automation tab from the left menu, which gives Demo Project or Configure Test Suite options.
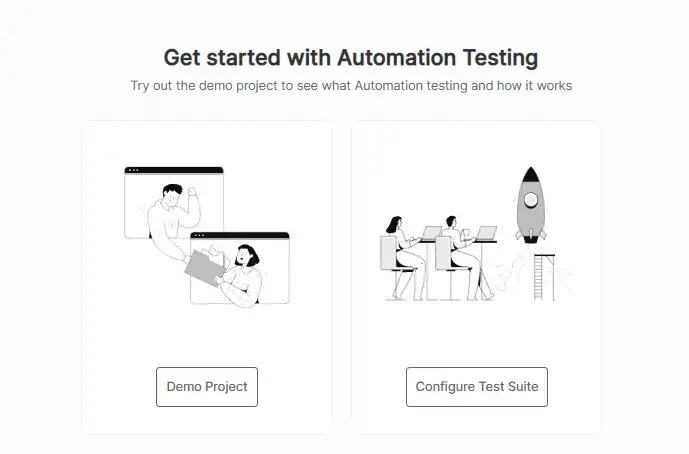
Step 3: Choose Configure Test Suite to run the test and select your preferred automation testing framework.
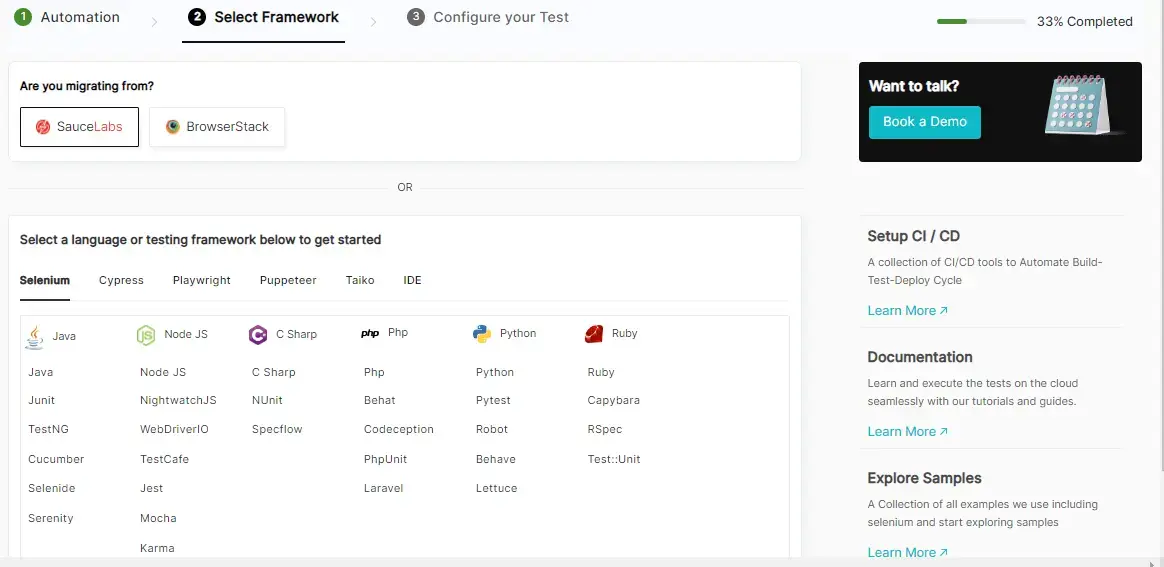
Step 4: Configure your test and start testing.
Challenges in Web Application Testing
In testing web applications, there are certain challenges that most developers and testers encounter and find difficult to address. This may lead to failure in completing web app testing, and the quality of the application may be affected. Hence, it is of utmost importance to be aware of the challenges of web application testing:
Uncontrolled web app environments: Web applications run on various platforms, screen resolutions, browsers, and devices, making it difficult to achieve comprehensive test coverage across all environments. Testers must carefully evaluate and prioritize the most relevant combinations for testing based on user demographics and usage patterns.
Frequent UI change:Web applications undergo regular updates, introducing new features, third-party integrations, or changes to the user interface. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging for testers, as it requires maintaining and updating test scripts to align with the evolving UI, ensuring proper test coverage, and avoiding script failures.
Handling image comparisons: Web automation often involves comparing images for visual validations. Managing image comparisons can be complex, as variations in pixel details, such as shape, size, and color, must be carefully handled to ensure accurate and reliable image conversions for testing purposes.
Usability issues: Usability problems can significantly impact the success of a web application. When multiple features are squeezed into limited-screen real estate, usability can be affected. Testers must employ proper usability testing tools and techniques to create comprehensive test plans focusing on seamless navigation, intuitive user interfaces, and meeting user expectations.
Best Practices of Web Application Testing
The challenges mentioned above in web application testing can be mitigated by following the below best practice:
Test on different browsers and devices: You should test your web application on a variety of browsers (such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge) and devices (desktop, mobile, tablets). This ensures your application functions correctly and looks consistent across different platforms, providing a seamless user experience.
Test for scalability and load handling: Always perform scalability and load testing to assess your web application's performance under heavy user loads. Simulating high user traffic will help identify performance bottlenecks, such as slow page load times or crashes, and allows you to optimize your application's performance accordingly.
Perform security audits: You should conduct security audits to find any potential vulnerabilities, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), or authentication flaws. It is important to implement proper security measures, such as secure coding practices and encryption, to protect your application and user data.
Implement continuous testing practices: Embrace continuous testing methodologies, such as continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), to ensure that your web application is continuously tested throughout the development lifecycle.
Validate user input and data handling: Thoroughly test user input fields, form submissions, and data handling processes to ensure data integrity and prevent common issues like data loss, incorrect calculations, or validation errors. Validate input against expected formats, perform boundary value analysis, and handle error conditions gracefully.
Test for accessibility: Pay attention to web accessibility standards and guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), to ensure that your web application is accessible to users with impairments. Test for screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation, color contrast, and other accessibility features to provide an inclusive experience for all users.
Monitor and analyze application performance: Continuously monitor your web application's performance using tools like Application Performance Monitoring (APM) or web analytics. Monitor key metrics such as response time, server load, and error rates to identify and proactively address performance bottlenecks.
Conclusion
Web app testing plays a crucial role in ensuring web applications' quality, functionality, and security. It helps to identify and rectify issues early in the development lifecycle, reducing the risk of costly bugs or vulnerabilities in production.
It ensures that the application functions as intended, provides a seamless user experience across platforms, and handles varying user loads effectively.
Organizations can deliver robust and reliable web applications by following best practices such as testing on different browsers and devices, performing scalability and load testing, conducting regular security audits, and implementing continuous testing practices.
As technology evolves, web application testing must adapt to emerging trends and challenges, such as cloud infrastructure, mobile responsiveness, and the increasing complexity of web applications. Organizations can continuously improve their web application testing processes and deliver high-quality applications that meet user expectations by staying updated with the latest testing methodologies, tools, and best practices.
